The rise and advances of new automation and artificial intelligence software algorithms, including those that learn predictive models from historical data, are making increasingly consequential predictive decisions. Such decisions are having an impact on the lives of people in domains as diverse as digital media, advertising, finance, credit, employment, education and criminal sentencing.
Marketers and companies need to understand that we are entering into a new generation of optimizing websites for search engines.
As far as the adage, “SEO is Dead”, it is NOT. But, as Bob Dylan stated in 1964, “The Times They Are a-Changin”.
While many principles and tactics stay the same in search engine optimization, we cannot deny the current path of technological breakthroughs, such as the introduction of complex machine learning algorithm systems like Google’s RankBrain.

In this guide post I will cover:
- What RankBrain is, exactly
- How search results are being changed
- How a brand can evolve their digital marketing strategy for machine learning search algorithms
- Why using PPC advertising might be more important than ever
An Intro to Google’s RankBrain
RankBrain is a machine learning artificial narrow intelligence system that was introduced to the public in 2015. Bloomberg was the first news publication in mainstream media to break Google’s newest search ranking factor called RankBrain, first with an interview with Greg Corrado, a senior research scientist at Google.
And while the public officially met RankBrain in 2015, Google’s Matt Cutts (former webmaster), had been mentioning it as early as 2013.
RankBrain is designed to better understand the meaning behind the words a person uses and types into his or her search engine. This Google blog post discusses this concept into trying to better understand word relationships. You will definitely want to learn more about this technology!
From the aforementioned Bloomberg interview and article, we came to learn that 15% of queries per day have never been seen by Google before, and RankBrain is helping to interpret those obscure search queries. Bruce Clay, a veteran SEO marketer, discusses how SEOs should approach RankBrain in this podcast.
The Rise of Mobile: a Primary Driver of RankBrain’s Existence?
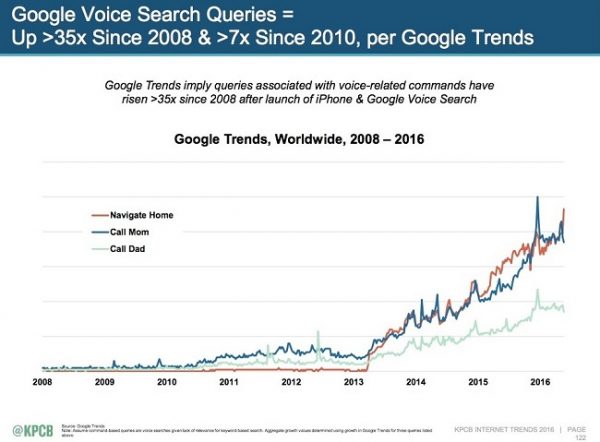
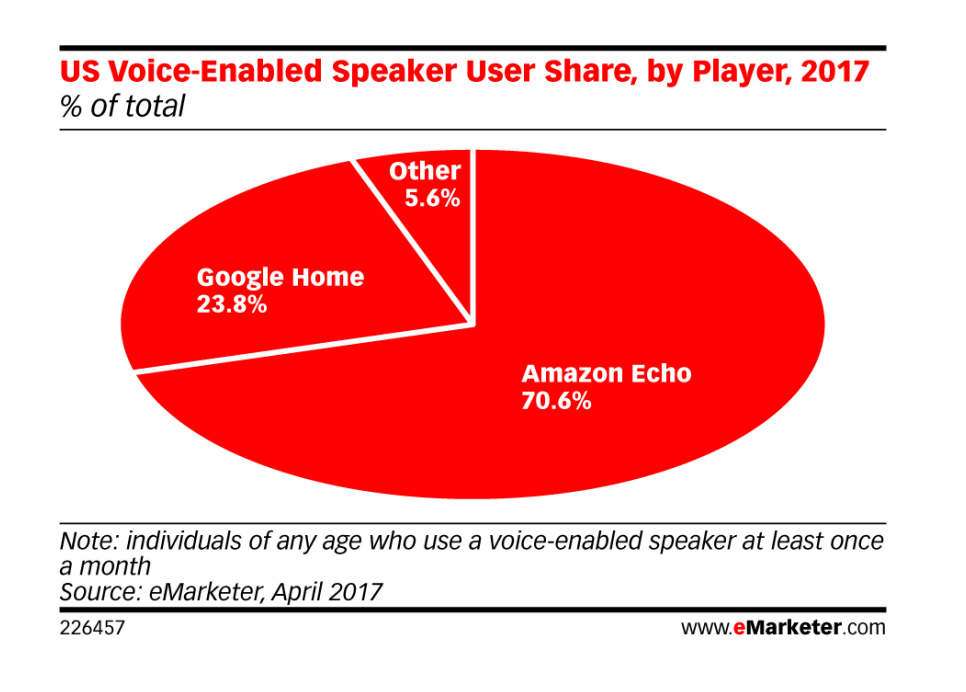
It seems as though mobile search drove the need for RankBrain even further than Google thought it would. Mobile search behavior has been a game changer, especially when it comes to voice search (Siri, Alexa, etc), something most smartphone users take advantage of.
As you may know, most queries tend to be much more conversational using voice search versus typing when using a computer device.
RankBrain deals well with the conversational long-tail queries that are common to voice search today, although there are still plenty of long tail searches typed into Google’s search bar, as well.
I believe that RankBrain is preparing for the world where voice search will become more and more the norm.

A Rundown of What RankBrain Actually Does
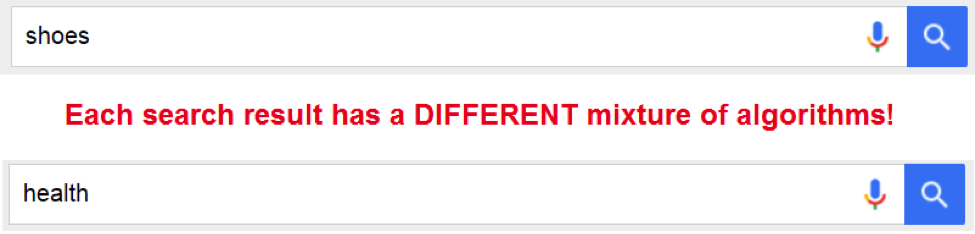
For example, in certain search results, RankBrain might learn that the most important signal is the Meta Title. Adding more significance to the Meta Title matching algorithm might lead to a better searcher experience. But, in another search result, this very same signal might have a horrible correlation with a good searcher experience. So, in that other vertical, another algorithm, maybe PageRank, might be promoted more.
Along with the ability to better understand concepts on a web page, RankBrain also allows for a better understanding of the association between multiple queries, such as:
“Where is the Empire State building?”
Followed by:
“How tall is it?”
How Does RankBrain Actually Learn? Examples of RankBrain in Action.
Basically, RankBrain can take sets of “training” data created by human engineers to help establish a baseline. It can then apply controlled machine learning to determine the best search results on a variety of factors over time. Google also confirmed, in the same aforementioned Blomberg article, and later in this article by Danny Sullivan , from Search Engine Land, that Google frequently updates the system by feeding it new data to better reason with new concepts.
During an SMX West Expo conference, speakers Marcus Tober, founder of Searchmetrics, and Eric Enge, CEO of Stone Temple consulting, respectively, shared examples of RankBrain working in action.
One of the studies mentioned showed how RankBrain better interpreted the relationships between words. This can include the use of stop words in a search query (“the,” “and,” without,” etc) — words that were historically ignored previously by Google but are sometimes of a 
Let’s say we use the example of the comedy TV series “The Office”. This is an example of a search that would be taken out of context without reading and incorporating the all-important “the” word if it was indeed typed into to the search box.
Another example explained by Gary Illyes, a Google web trends analyst, in an interview notes: “Can you get 100% score on Super Mario without walk-through?” Ignoring “without” would potentially return search results on getting a 100% score on Super Mario with a walk-through…in essence, the opposite results a person was trying to get via the search query.
There are other theories on how RankBrain might use data to learn to show the best results for a query. It is also completely possible that a searcher’s engagement with the search result might be a factor in how RankBrain determines the relevancy of a result, as Rand Fishkin founder of Moz, suggests in a keynote last July 2016.
For example, if someone clicks a search result and doesn’t hit the back button (pogo-sticking), and return to the search results to start clicking on other website pages, this could be an indication to Google, that the searcher found what he or she was looking for.
Thus the machine could then presumably learn over time that a low bounce rate signals a relevant result so that web page could show up more often and be shown higher in search results related to that query.
Here’s a visual of that concept from Rand Fishkin’s keynote presentation:
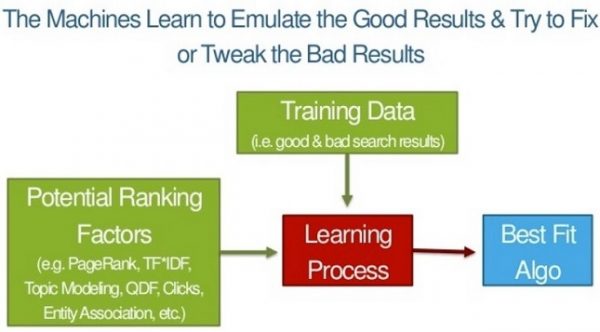
How RankBrain Works with Other Google Algorithm Ranking Signals
As mentioned earlier in this guide post, RankBrain is essentially built into the Google query process to better understand language and make
Remember, as mentioned by many “Googlers,” Google still uses hundreds of other ranking signals that it can apply to a search query to identify the best results.
In 2016, a Googler named Andrey Lipattsev confirmed that RankBrain was now among it’s top three ranking signals for search, along with links and content as the other two most influential factors. This is an important concept for marketers and business owners to understand. Google clearly stated that the signals that the SEO marketing world believes to be important still matter quite a lot: quality content and authoritative links.
While the content on a website and its links are both vital to determining meaning and relevance, RankBrain works in partnership by assisting the Google search engine to better determine if a website is the most relevant to the searchers implied intent–based on signals and algorithms. According to Aleh Barysevich the CMO of Link-Assistant.com, there are 7 ways Google rewrites search queries behind the scenes to produce better search results.
The Impact RankBrain has for Big Brands
With machine learning, RankBrain learns associations over time. This means that if a brand becomes associated with a certain product, the queries about that product may lead to more branded search results. Because Google tends to favor or give preference to bigger brands for a variety of reasons, with RankBrain metrics like a site’s engagement rate, mentions of the brand across multiple social media sites, and so on, may further enhance partiality. This may also happen in spite of the fact that some larger brands may have a weaker link profile than some other competitor websites in their respective industry.
What RankBrain Means for Your SEO and Online Marketing Strategy
OK, now for some action items …
SEO and Your Content
First, let’s discuss content. For many marketers, it’s actually just business as usual. You should examine your content to ensure it provides the best, most comprehensive answers to satisfy a particular query, whether you are trying to rank for an informational page or selling a product or service.
RankBrain is a machine learning system, but it still needs input from your site. It’s working better to understand and make connections about concepts. For example, we can give RankBrain credit for understanding a page is about basketball even if the words, and only the words, “Golden State Warriors” and “Cleveland Cavaliers” are present on a page.
One of the goals of SEO is to better help search engines understand what your content is about. It is still crucial that you make sure to include the keywords that are relevant and important to your company on your website’s pages. This includes “stemming” keywords (like “walked” and “walking” along with “walk” and “walks”) while using synonyms and natural word variations to help make connections between ideas.
Another example of this could be the word “mercury.” You could use this word “mercury” 12 times on a page, but if you forget to use the word “planet”, then the search engine may be confused about the subject of the page. Is it an element, a car, insurance or something else?
This is when the time for exploring and implementing structured data markup, which helps search engines to better make connections as to what a page is about more easily, is essential.
Remember, the Little Things Matter as they Always Have in Search Engine Optimization
You will want to continue to pay attention to make sure your search results listings stand out from the crowd if one of your marketing goals includes ranking on the first page. That means ensuring each web page has unique metadata in addition to exploring other ways you can make your page stand out; using schema markup and useful, engaging content.
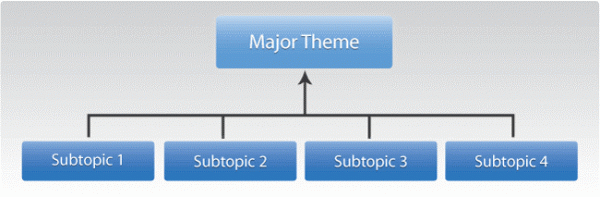
Another question to ask: once people land on your website, is it helping them move farther along in their journey by offering up related content that explores a topic/product/service or more? This can be done by siloing your content to create subject themes around the key terms that will help your website rank on search results pages for your business.
 RankBrain and Digital Marketing Strategies
RankBrain and Digital Marketing Strategies
I mentioned earlier that RankBrain will likely favor big brands. So what happens if you are a startup or small business?
Now is the time to start thinking about improving your online marketing team and strategy, if you haven’t already. While it’s a great idea to have a robust and thorough SEO and content marketing strategy, it’s never a great idea to put all of your eggs or marketing budget in one basket, so to speak.

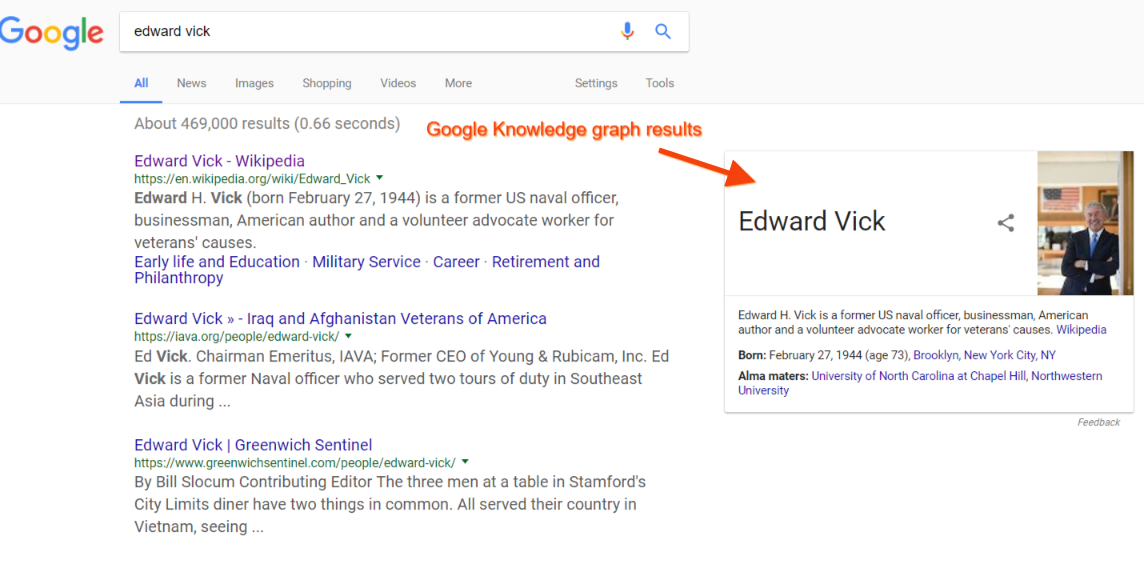
 Become a Knowledge Graph entity
Become a Knowledge Graph entity
Google’s semantic search is powered by the Knowledge Graph in numerous ways. The Knowledge Graph is a collection of entities – specific objects that Google knows a few things about, such as persons, places, and things. The Knowledge Graph’s impact on search results stretches far beyond the branded panels that are sometimes displayed to the right of organic listings. Knowledge Graph data is used in organic rankings, rich answers, and various query-specific types of search results.
 Critical Technical SEO Issues to Examine
Critical Technical SEO Issues to Examine
In the age of RankBrain, these foundational technical SEO issues still matter.
Prioritizing an SEO to do list is is important for business. Focus your resources on SEO work that is actually going to improve rankings, increase clicks and drive revenue. Most companies should focus on engagement SEO work, but technical tasks can’t be ignored completely — especially if you have major problems, such as any of these listed below:
- Site speed. Google has said that site speed is a ranking factor, and study after study continues to show that faster sites rank better, get more engagement and close more business. Google’s own research shows that most mobile users abandon a site that takes longer than three seconds to load.
- Mobile performance. In addition to site speed, every other aspect of a site’s mobile performance is an important technical consideration as well. With mobile-first indexing right around the corner, mobile deserves its own discussion (see below).
- Blocked resources. If search engines can’t index or crawl your site, resolving this issue should be your first priority. Allowing site content to be indexed is one of the quickest ways to improve incoming organic traffic. Crawl issues may be caused by a few factors: an error in your robots.txt file, unintentional noindex tags in site metadata or server issues that limit Googlebot’s crawl rate.
- Google penalties. Hacked sites, spam content and unnatural backlink profiles can all lead to severe ranking penalties. Sites with manual actions can be demoted in search results or removed altogether. If the Google Search Console lists a manual action on your site, take steps immediately to resolve the issue — disavow low-quality links and delete hacked or spam pages — and submit your site for reconsideration.
- Significant URL and/or redirect problems. Did you launch a new site and forget to implement redirects? Perhaps that was two or three launches past, and those problems were never fully resolved? Is your site generating thousands of meaningless unique URLs? When URL and redirect problems reach a critical mass, they can pose a significant risk to your organic traffic.
- Your site isn’t optimized for mobile. Mobile-friendliness is already a ranking factor for mobile search, and mobile-first indexing is about to make it important all around. Your site has to fit on a mobile screen, load fast enough for a mobile audience and be free of mobile errors.
- Your content isn’t optimized for mobile. Transitioning your site to a mobile-friendly format is only the first step in improving mobile usability. The content itself needs to be designed for the mobile user. Make sure that buttons and links that are large enough for thumbs to tap, write content in shorter paragraphs, center-align images and maybe even vertically align media.
- Lack of conversions. If the content on your site doesn’t cater to your visitors’ intent, conversions will suffer. So, the most critical engagement SEO task on your list should be reviewing existing content against keyword/user intent research. It’s possible that customers at the top of the purchasing funnel are finding content that caters to the bottom- they’re not converting because your content didn’t satisfy their needs.
- Low click-through rate (CTR) in spite of high rankings. If your CTR is low on pages with high rankings, it’s possible your competitors are stealing traffic with featured snippets. Featured snippets offer an opportunity to drive organic traffic by ranking in position “zero”. Perform a depersonalized search of your keywords and see if competitors appear in position zero. If so, prioritize optimizing existing content for featured snippets.
RankBrain Is Not the End of SEO but it is Changing it
If your company is worried about how RankBrain impacts SEO, there is quite possibly more to worry about than you may think.
RankBrain is search results relevance on steroids. Simply put, you must improve your content relevancy to match the query intent. Yes, SEO best practices are crucial to traffic, and rankings are competitive than ever.
But, it’s also important for startups to focus their content marketing strategies, from a macro and micro level, and how your website’s content (as a whole) helps to answer the questions your audience is looking for.
And don’t forget to supplement your digital marketing strategy with things like paid search, remarketing social and other channels to keep your brand top of mind.
Technology is advancing rapidly, and buyer expectations and demands are evolving alongside these innovations. Today’s critical SEO priorities will be tomorrow’s outdated practices because search engines are designed to cater to people, and people change. A few SEO takeaways to keep in mind:
- Each competitive keyword environment will need to be examined on its own
- Most sites will need to stay niche to avoid misclassification
- Each site should mimic the structure and composition of their respective top sites in that niche
Do you have insights on the impact of RankBrain on search rankings? I want to know. Leave a comment below.



 RankBrain and Digital Marketing Strategies
RankBrain and Digital Marketing Strategies
 Critical Technical SEO Issues to Examine
Critical Technical SEO Issues to Examine